The past year’s wars in the Middle East have long been complex and devastating, shaped by a multitude of factors. In recent years, a new player has emerged on the battlefield: artificial intelligence (AI). AI’s role in these conflicts is multifaceted, offering both potential benefits and risks that deserve careful consideration.
National security relevant AI systems broadly fall into two categories: upstream tasks, such as intelligence, surveillance, and information management; and downstream tasks, such as target selection and engagement.
On the Offensive Side
Over the past few years, the world has seen an ever-growing AI arms race, as countries and militant groups scramble to develop advanced AI systems for drones, targeting systems, and land and sea-based weaponry. We have seen a dramatic increase in the use of complex AI systems to bolster warfare capabilities and these are being used right now in the Middle East’s deadly conflicts.
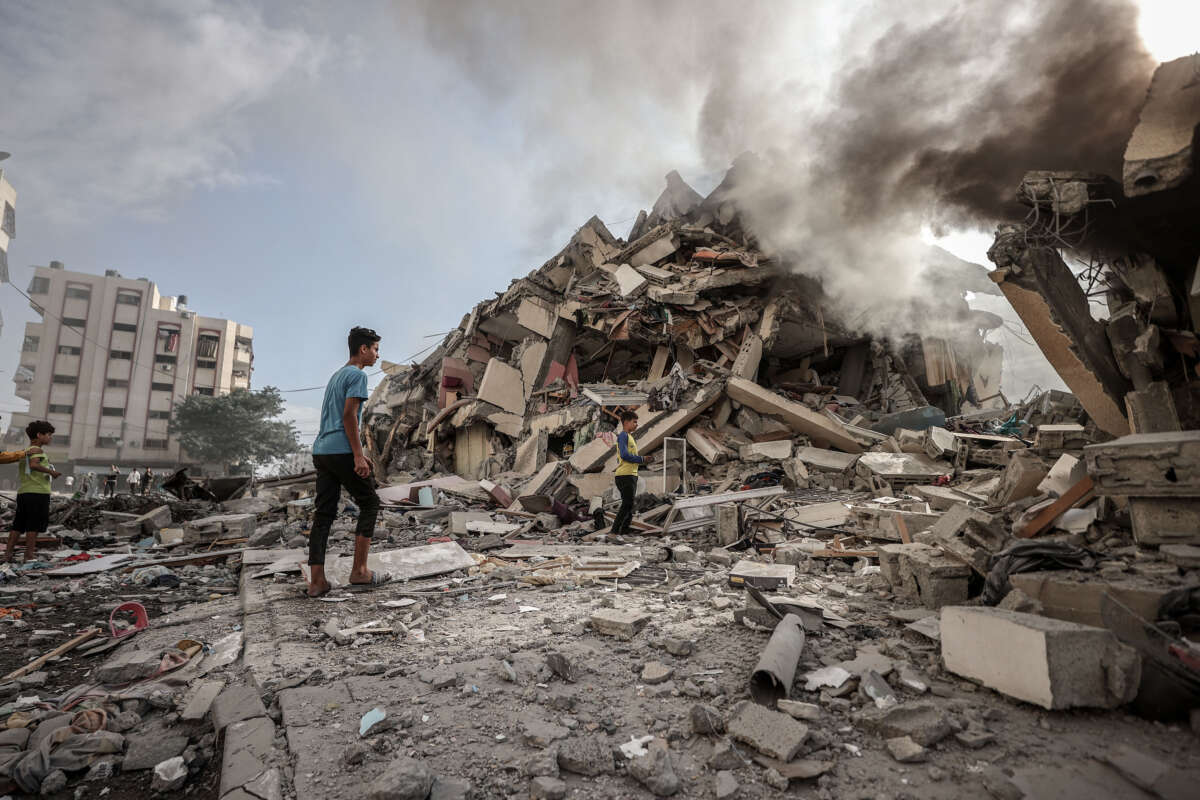
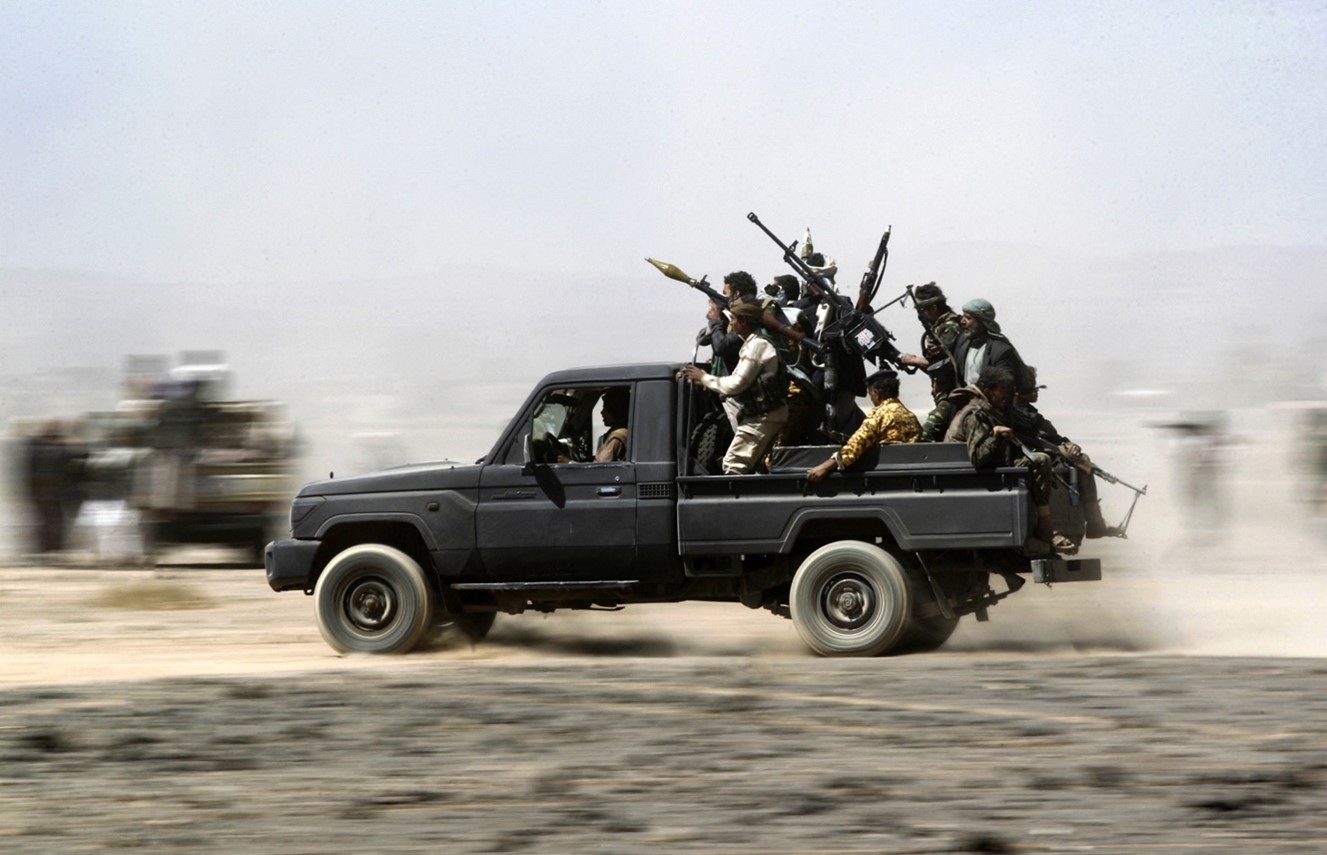
- Drones and Autonomous Weapons: Armed drones equipped with AI-powered targeting systems have become a mainstay in Middle Eastern conflicts. From Israel’s use of kamikaze drones in Gaza to Houthi rebels attacking Saudi Arabia’s oil infrastructure, these unmanned aerial vehicles raise concerns about civilian casualties, accountability, and ethical warfare.
- Cyberwarfare: AI plays a crucial role in cyberattacks, allowing for automated reconnaissance, vulnerability identification, and even the development of self-propagating malware. This form of warfare can cripple infrastructure, disrupt communication networks, and sow widespread chaos.
- Intelligence Gathering and Analysis: AI algorithms can sift through vast amounts of data from satellites, drones, and social media, providing valuable insights into troop movements, enemy planning, and potential threats. This intelligence can be crucial for targeting enemy forces and making strategic decisions.
On the Defensive Side
Israel’s Iron Dome defence system, an all-weather air defence system designed to intercept and destroy short-range rockets and artillery, before they reach their Israeli targets.
Recently, the Iron Dome has been upgraded with new AI capabilities to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the system and more effective against a wider range of threats. AI-powered algorithms are now used to analyse intelligence from radar and other sensors to track incoming weapons and determine the best time to intercept, increasing the Iron Dome’s success rate to over 90%.
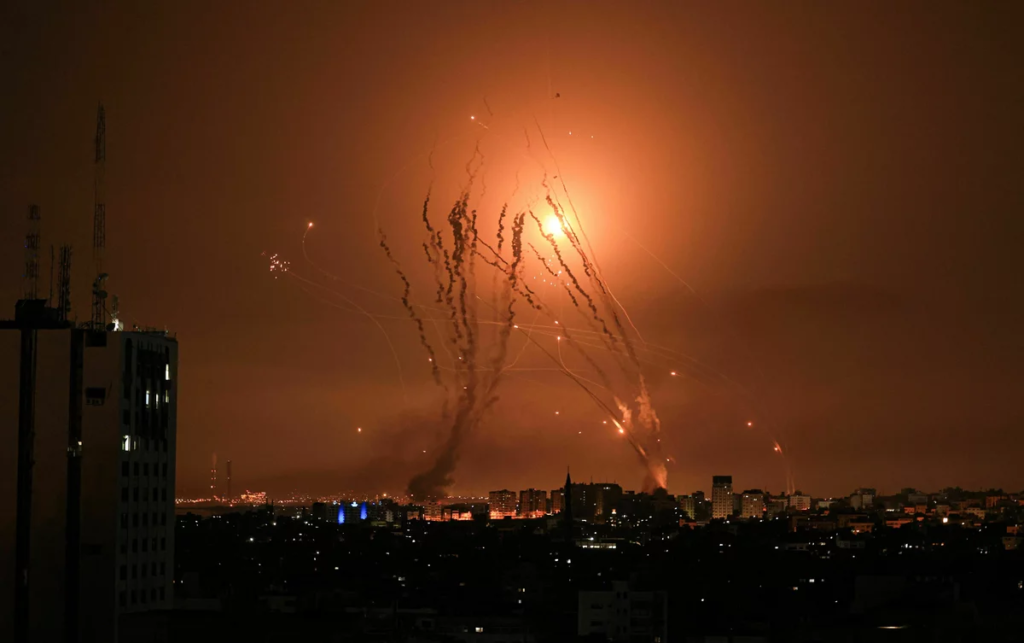

Mahmud Hams/AFP via Getty Images
How else is AI being used by nation states to protect civilians and critical infrastructure from hostile actors?
- Missile Defence Systems: AI-powered missile defence systems like Israel’s Iron Dome have proven highly effective in intercepting incoming rockets and artillery shells. This technology helps protect civilian populations and critical infrastructure from attack.
- Cybersecurity: AI can be used to develop advanced cybersecurity tools that detect and thwart cyberattacks. This is crucial for protecting sensitive military and government networks from infiltration and sabotage.
- Logistics and Support: AI algorithms can optimize logistics operations, manage supply chains, and predict maintenance needs for military equipment. This can improve efficiency and ensure that vital resources reach the front lines when needed.
The Other Side of the Coin
While AI offers undeniable advantages in modern warfare, its use raises significant ethical concerns. The potential for autonomous weapons systems to operate without human oversight raises questions about accountability and the risk of unintended consequences. Additionally, the use of AI in cyberwarfare can blur the lines between military and civilian targets, potentially leading to widespread and unacceptable collateral damage.
The Future of AI in Middle Eastern Wars
As AI technology continues to evolve, its role in Middle Eastern conflicts is likely to become even more significant. Managing the risks and maximizing the benefits of this powerful tool will require careful international cooperation, robust ethical frameworks, and a commitment to responsible use.
Ultimately, the decision of whether AI becomes a force for good or ill in the wars of the Middle East rests with humanity itself. We must approach this technology with both caution and vision, ensuring that it serves the cause of peace and security for all.