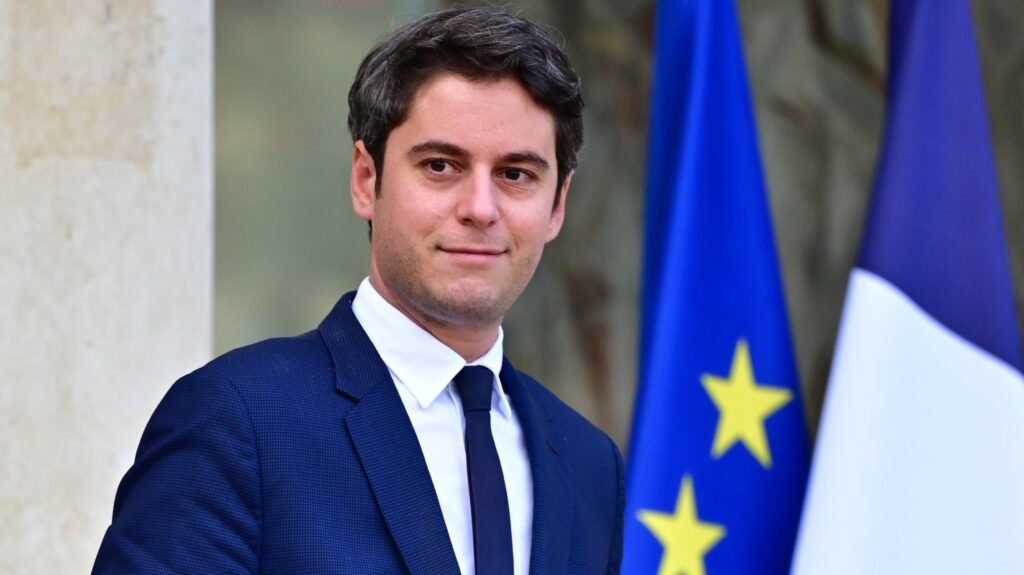
Navigating France’s National Security Landscape: Who is Gabriel Attal, France’s New Prime Minister?
Gabriel Attal, France’s new Prime Minister and the youngest person to ever hold this position, is not a name typically associated with France’s national security strategy. However, in his current and previous roles (Attal has moved to the premiership from the role of Minister of Public Action and Accounts), Attal has emerged as a key figure in the country’s approach to tackling emerging threats and safeguarding its citizens.

Why is this Important? A Shift in Focus
Following the 2020 beheading of a teacher by a Chechen extremist, France has prioritised the fight against terrorism and radicalisation. Attal’s focus, however, extends beyond traditional notions of national security. He recognises the interconnectedness of challenges like cybercrime, climate change, and health emergencies, advocating for a more comprehensive approach.
Cybersecurity at the Forefront
Attal has identified cybersecurity as a top priority, emphasising the need for robust defences against online attacks that could cripple critical infrastructure or disrupt essential services. His efforts have included:
- Investing in cyber defence capabilities: France has increased funding for its cyber defence agency, ANSSI, and established a national cyber security strategy.
- Promoting international cooperation: Attal has championed international collaboration on cybersecurity, recognising that no country can effectively combat cyber threats alone.
- Raising public awareness: The French government has launched initiatives to educate citizens about cybersecurity best practices and the potential risks of online threats.
Beyond Traditional Threats
Attal’s vision for national security extends beyond immediate threats like terrorism and cyberattacks. He acknowledges the long-term implications of climate change and pandemics, calling for proactive measures to mitigate their impact.
- Climate resilience: Attal has emphasised the need for France to prepare for the security challenges posed by climate change, such as natural disasters and mass displacement.
- Pandemic preparedness: The COVID-19 pandemic highlighted the importance of robust public health systems and international cooperation in addressing global health threats. Attal has advocated for strengthening France’s preparedness for future pandemics.
Challenges and the Road Ahead
Attal’s comprehensive approach to national security faces several challenges. Balancing immediate threats with long-term challenges requires careful allocation of resources and political will. Additionally, fostering international cooperation requires overcoming differences in priorities and approaches among various countries.
Despite these challenges, Attal’s efforts to broaden the scope of France’s national security strategy represent a significant step forward. By recognising the interconnectedness of emerging threats and prioritising both immediate and long-term challenges, Attal is laying the groundwork for a more resilient and secure future for France.
In Conclusion
Attal’s approach to national security has been controversial – as Education Minister, Attal banned abayas in schools. But it also reflects a growing understanding of the complex and evolving nature of threats facing France and the world. His focus on cybersecurity, climate resilience, and pandemic preparedness highlights the need for proactive and comprehensive strategies to safeguard citizens in the 21st century. While challenges remain, Attal’s efforts offer a promising model for navigating the increasingly intricate landscape of national security.