Franco-British missile firm targeted by cybercriminals who demand £273k for stolen data
Stolen missile data, which purports to include blueprints of weapons used by NATO allies in the Russia-Ukraine war, is being offered for sale on Russian and English hacker forums, it has emerged.
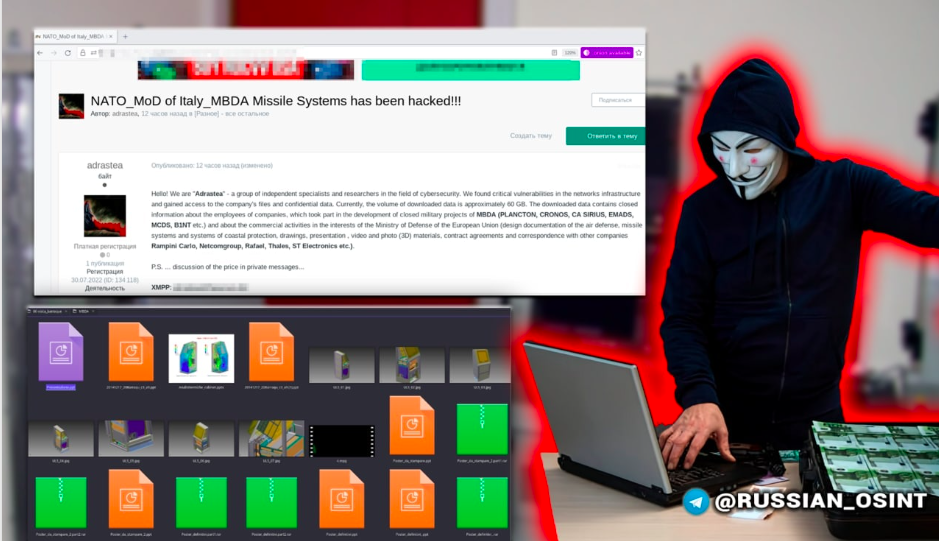
A cybercriminal group, using the pseudonym of Adrastea, is pricing the haul at 15 bitcoins (equivalent to £273,000) for 80GB of stolen intelligence and has allegedly been met by one unknown buyer so far.
Adrastea claimed to have found “critical vulnerabilities in the network infrastructure” of Franco-British MBDA, the world’s second largest missile maker.
The classified military documents were hacked from a compromised hard drive belonging to a supplier of the firm, and allegedly relate to employees involved in projects such as EMADS (Enhanced Modular Air Defence Solutions) and MCDS (Mobile Coastal Defence System).
The European company, which has bases in the UK, France and Italy, admitted its data was among the stash, but denied that any of the classified files belong to it.
Police in Italy are investigating the data breach, and a NATO official confirmed they are following the investigation closely.
“We are assessing claims relating to data allegedly stolen from MBDA. We have no indication that any NATO network has been compromised. NATO takes all the necessary measures to keep our networks safe,” they added.
Yesterday, investigative journalists from the BBC claimed to have been offered a 50MB sample of the stolen data. Documents seen were labelled “NATO CONFIDENTIAL,” “NATO RESTRICTED” and “Unclassified Controlled Information.” In addition to the sample, the criminals supplied documents by email, including two marked “NATO SECRET”.
Nato’s classification levels are:
- COSMIC TOP SECRET: unauthorised disclosure would cause exceptionally grave damage to NATO.
- NATO SECRET: unauthorised disclosure would cause serious damage to NATO.
- NATO CONFIDENTIAL: unauthorised disclosure would be damaging to NATO interests.
- NATO RESTRICTED: unauthorised disclosure would be disadvantageous to the interests of NATO.
- Unclassified Controlled Information is a US security label for information that is government created or owned; information that requires safeguarding or dissemination controls consistent with applicable laws, regulations and government-wide policies.
The hackers refused to say whether the material had come from more than one source. One file, seen by the BBC, detailed a “communications intelligence” flyover by a US air squadron at the end of 2020 in Estonia.
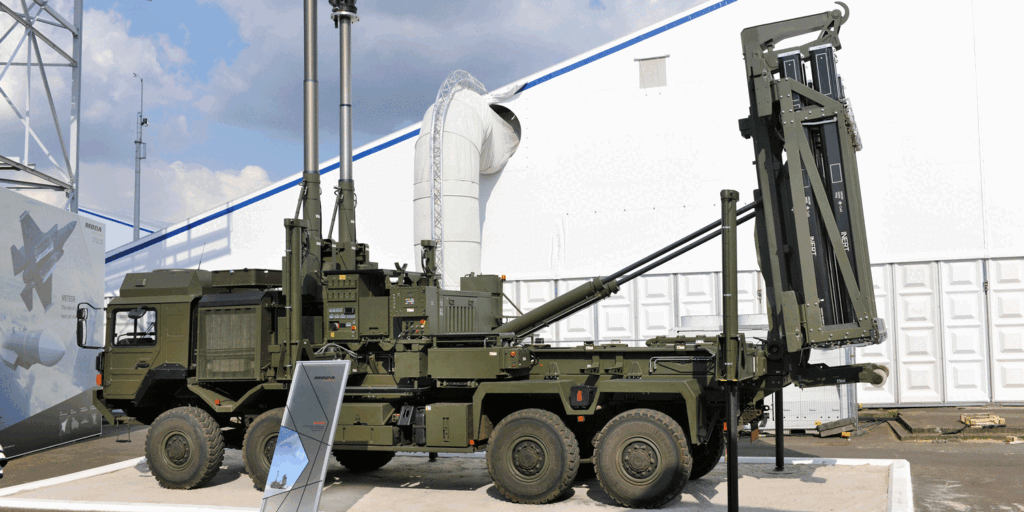
Among the stolen cache were sample files detailing the workings of the Land Ceptor/CAMM (Common Anti-Air Modular Missile) which was recently sent to Poland for use in the Ukraine conflict.
The missile group is owned by France’s Airbus and Britain’s BAE Systems, both with a 37.5% stake, and by Italy’s Leonardo, with a 25% stake. Last year it enjoyed record results.
The consortium posted 4.2bn euros ($4.54bn) in revenue last year and new orders were worth 5.12bn euros.
MBDA has some 16% of the global missile market, in terms of orders, but is the largest player in Europe, with a 43% share.
In a statement, the MBDA said: “No hacking of our secure networks has occurred. MBDA can confirm that there is no protectively marked data from MBDA involved.”